Instructions
Configure a persistent USB connection
Since I’m using a headless Debian Bookworm setup, I need to properly configure the USB drive so that it automounts and is accessible after every reboot. I’ve already created an instructions that work pretty well for me.
Unistall conflicting Docker packages
Start by uninstalling all previous versions or conflicting versions of Docker. The docker website suggests doing this as some Linux distros come with some packager installed:
for pkg in docker.io docker-doc docker-compose podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get remove $pkg; done
If you want to start with a clean install base, then follow the process described on the Docker website here.
Install Docker on the RPi
There’s a lot of documentation on the web, including the Docker website here, on how to install Docker on a Raspberry Pi, but I still had trouble completing the installation, as the latest and greatest version had my older RPI-3 deprecated.
As I searched for older versions to install, I ran into this page, which met my needs. It’s also much simpler.
> sudo apt-get update
> sudo apt install docker.io
The command installs a Docker package that's maintained by Debian/Ubuntu/Raspberry PI OS repositories that has better compatibility with older ARM architectures. Functionally, this should meet my needs with Navidrome.
After the RPi settled down, I typed the following to see if the docker service was running:
> sudo systemctl docker status
And the RPi replied that docker was active (running). Then I typed:
> sudo docker run hello-world
to which, the RPi returned the anticipated message that:
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
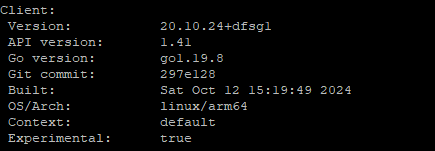
Then I checked the version of the installed package with:
> docker version
and the system told me that I had version 20.10.24+dfsgl
Success!
Create directory structure for Navidrome
Create a directory for the Navidrome Setup:
> mkdir -p ~/docker/navidrome
Navigate to the directory with:
> cd ~/docker/navidrome
and create one more directory for persistent data:
> mkdir -p data
Install Docker Compose
docker-compose is a tool used to define and manage multi-container Docker applications using a simple YAML file (docker-compose.yml). It lets you configure all your containers, networks, and volumes in one place, and start them all with a single command.
Check if Docker Compose is installed:
> docker-compose --version
If it's not installed, the following message appears:
> -bash: docker-compose: command not found
I went ahead and installed it with the following command:
> sudo apt install -y docker-compose
and checked the install version again, and saw the following message:
> docker-compose version 1.29.2, build unknown
Create docker-compose.yml file
I created the docker compose file with:
> nano docker-compose.yml
version: '2'
services:
navidrome:
image: deluan/navidrome:latest
container_name: navidrome
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "4533:4533" # Port for Navidrome (won't conflict with WordPress)
environment:
- ND_SCANSCHEDULE=1h
- ND_LOGLEVEL=info
volumes:
- ~/docker/navidrome/data:/data
- /path/to/your/music:/music:ro
Before we continue, a quick note: Why Version 2:
The version field specifies which version of the Docker Compose file format that I'm using.
In this case, with the Raspberry Pi 3 running Docker through docker.io, version: '2' is a good choice because:
- It's widely compatible with older Docker installations
- It provides all the features you need for Navidrome
- It's less resource-intensive than version 3, which is optimized for swarm deployments
Start Navidrome
I made sure that in the same Navidrome directory that I just created: ~/docker/navidrome
Then I started the container using the following command:
> docker-compose up -d
If things go as planned, then the script will download the Navidrome image and create and start the container.
> Creating network “navidrome default” with the default driver
> Pulling navidrome (deluan/navidrome:latest)...
> latest: Pulling from deluan/navidrome
When complete, verify that the container is running, with:
> docker ps
The response should be a table with headings and information for CONTAINER ID, IMAGE, etc.
You can also view the logs with:
> docker logs navidrome
which will pour a ton of stuff on the screen starting with an ASCII image that says "NAVIDROME"
Access Navidrome
Use your favourite web browser to navigate to Navidrome. Include the port number in the URL:
http://your-rpi-ip:4533
Useful Information
Debugging Docker Compose installation
The first time I ran docker-compose, I received a traceback that ended with an error saying:
docker.errors.DockerException: Error while fetching server API version:
Here's how I debugged the issue with some help from Claude:
Check if docker is running with:
> sudo systemctl status docker
The response was that Docker was active (running)
I checked the Docker version.
Checked Docker socket permissions with:
> ls -l /var/run/docker/sock
And the answer was:
srw-rw---- 1 root docker 0 May 14 13:11 /var/run/docker.sock
I added my user to the Docker group with:
> sudo usermode -aG docker $USER
And rebppted the RPi to apply the changes. After it came back up, I confirmed that the Docker Compose install was good by checking the version. And Docker Compose was ready for use.

